
A the trade-in value of an asset at the end of its useful life C how much an asset may be worth as scrap at the end of its useful life. 1 The book value of a plant asset is obtained by subtracting _____ from the _____ of the plant asset.
To find the book value of a plant asset you find the difference between the cost of the asset and the accumulated depreciation to date.
Book value of a plant asset. To find the book value of a plant asset you find the difference between whats the actual cost and its current depreciation date. Kindly follow these steps to get your riddle solved. Analyze the type of Book value.
Book value can be of any type you first need to determine what type of assets you hold and what are you going to get in the book value. Determine the actual cost of the plant asset. What Is the Book Value of Assets.
The book value of an asset is the value of that asset on the books the accounting books and the balance sheet of a company. Its also known as the net book value. Businesses can use this calculation to determine.
O Plant asset is scrapped or discarded. O Eliminate the book value of the plant asset at the date of sale by debiting accumulated depreciation and crediting the asset account for its cost. O Debit cash to record the cash proceeds from the sale.
O Compute gain or loss. If the cash proceeds the book value. Book value cost accumulated depreciation 40000-23000 17000 If book value cash received from selling transaction gain on sale of asset If book value cash received from selling transaction loses on sale of asset.
29 Revising Periodic Depreciation Net book value at date of change in estimate after 3 years. Equipment 13000 Accumulated depreciation 7200 Net book value 5800. Copyright 2019 John Wiley Sons Inc.
Sale of plant assets. Companies frequently dispose of plant assets by selling them. By comparing an assets book value cost less accumulated depreciation with its selling price or net amount realized if there are selling expenses the company may show either a gain or loss.
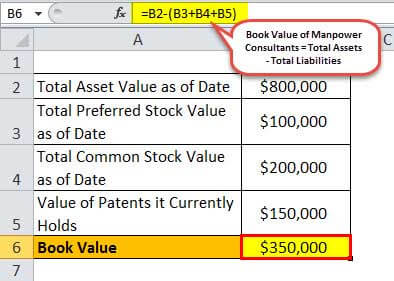
If the sales price is greater than the assets book value the company shows a gain. An assets book value is equal to its carrying value on the balance sheet and companies calculate it netting the asset against its accumulated depreciation. Book value can also be thought of as the net asset value of a company calculated as total assets minus.
A donated plant asset for which the fair value has been determined and for which incidental costs were incurred in acceptance of the asset should be recorded at an amount equal to its a. Book value on books of donor and. To find the book value of a plant asset you find the difference between the cost of the asset and the accumulated depreciation to date.
In selecting a depreciation method a. The book value of a plant asset is the difference between the. Replacement cost of the asset and its historical cost b.
Cost of the asset and the amount of depreciation expense for the year. 1 The book value of a plant asset is obtained by subtracting _____ from the _____ of the plant asset. 287 Bought 7 Share With.
1 The book value of a plant asset is obtained by subtracting _____ from the _____ of the plant asset. In a sale of plant assets the book value of the asset is compared to the proceeds received from the sale. If the proceeds of the sale exceed the book value of the plant asset a gain on disposal occurs.
If the proceeds of the sale are less than the book value of the plant asset sold a loss on disposal occurs. Is the total amount of depreciation for a plant asset that has been recorded up to a specific point in time. Book Value The original cost of a plant asset less its accumulated depreciation.
Carrying amount also called as book value of an asset is calculated by subtracting the accumulated depreciation from the cost of property plant and equipment. Impairment of an Asset An asset is impaired if the fair value of the asset is lower than the carrying amount book value of the asset. An accounting form on which a business records information about each plant asset.
The total amount of depreciation expense that has been recorded since the purchase of a plant asset. Book value of a plant asset. The original cost of a plant asset minus accumulated depreciation.
Gain on plant assets. The book value of a plant asset is always equal to its fair market value. Recording depreciation on plant assets affects the balance sheet and the income statement.
The depreciable cost of a plant asset is its original cost minus obsolescence. Recording depreciation each period is an application of the matching principle. The book value of an asset.
A the trade-in value of an asset at the end of its useful life C how much an asset may be worth as scrap at the end of its useful life. When the book value of a plant asset exceeds the cash received from sale proceeds the result is. Book value also carrying value is an accounting term used to account for the effect of depreciation on an asset.
While small assets are simply held on the books at cost larger assets like. The book value of a fixed asset asset is its recorded cost less accumulated depreciation. An old assets book value is usually not a valid indication of the new assets fair market value.
However if a better basis is not available a firm could use the book value of the old asset. Net book value NBV refers to the historical value of a companys assets or how the assets are recorded by the accountant. NBV is calculated using the assets original cost how much it cost to acquire the asset with the depreciation depletion or amortization.
Amortization Amortization refers to the process of paying off a debt through.