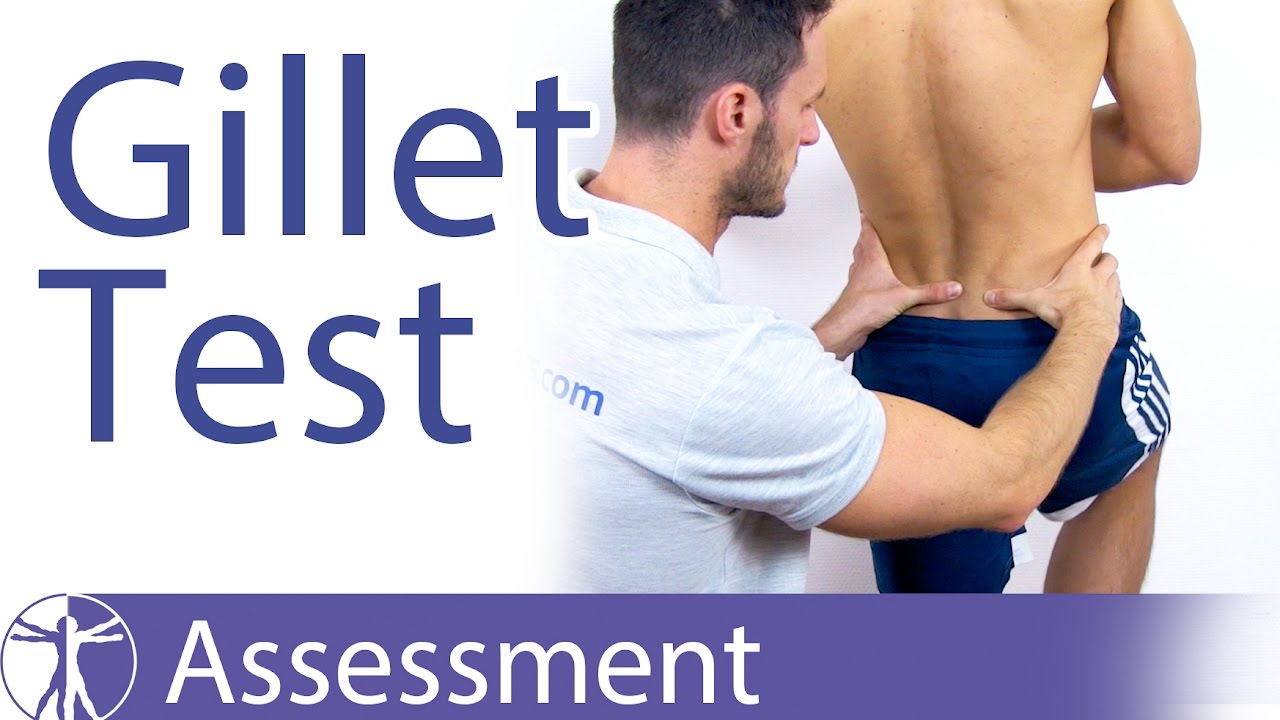
The Stork test also known as the Gillet Test assesses the movement of the SIJ between the innominate and sacrum through the clinicians palpation which may be a useful test for clinical evaluation of a subjects ability to stabilize intrapelvic motion. Home Courses Health Physiotherapy Sacroiliac Joint SI joint Assessment.

4 Many physical examination tests have.
Gillet test si joint. The Gillet Test for SI-Joint Dysfunction - YouTube. What is the Gillet test. The Stork test also known as the Gillet Test assesses the movement of the SIJ between the innominate and sacrum through the clinicians palpation which may be a useful test for clinical evaluation of a subjects ability to stabilize intrapelvic motion.
To assess mobility limitation in the sacroiliac region. The examiner palpates the inferior aspect of the PSIS of the tested side with one hand and the S2 spinous process with the other. The patient flexes the hip past 90 degrees.
The Gillet test is used to evaluate sacroiliac SI joint motion. The Gillet test is commonly performed by the clinician putting one thumb on the posterior iliac spine PSIS with the other thumb being placed on the sacral base SB in the area of the second sacral tubercle. How to assess motion of the Sacroiliac joint SIJ during the Stork or Gillet test - YouTube.
How to assess motion of the Sacroiliac joint SIJ during the Stork or Gillet test. The SI joint should be considered a potential pain generator and option for treatment in every case with low back pain. The diagnosis of SI joint disorders or at least the provocation tests should be included in every patient when they come in the door.
Biagio Mazza PT - paid consultant of SI-BONE. The flexion abduction external rotation FABER test is used to evaluate for pathology of the sacroiliac joint. A positive finding or this test is pain in the sacroiliac joint of the leg being tested.
What does a positive Patricks test mean. Pressue is applied on the superior aspcect of the tested knee joint lowering the leg into further. Test sacroiliac distraction see Fig.
413 below because this is the most sensitive test to detect inflammation in the joint. Apart from the positive sacroiliac distraction test attention. May be drawn to the sacroiliac joint by some discrepancies between gross symptoms and slight signs during standing lumbar movements.
Gillets test A clinical test used to identify sacroiliac SI joint pathology. Technique The patient stands with his or her posterosuperior iliac spines PSIS visible pulls one knee towards his or her chest and holds it while the examiner observes the PSIS. The anesthetic sacroiliac joint block hereafter referred to as the SI joint block has been identified as a controversial gold standard in the identification of pain originating from the SI joint.
4 Unfortunately this type of testing is not feasible for practitioners who lack training in joint injections and is not as cost-effective as a physical examination maneuver or maneuvers. 4 Many physical examination tests have. Home Courses Health Physiotherapy Sacroiliac Joint SI joint Assessment.
Sacroiliac Joint SI joint Assessment. Sacroiliac Joint SI joint Assessment. Patricks Faber Figure Four Test.
Piriformis Test Piriformis Syndrome or Tightness. Point specific tenderness at the sacral sulcus or posterior superior iliac spine is a consistent finding in sacroiliac joint lesions. Tests for sacroiliac joint can be divided into motion palpation tests and pain provocation tests.
Gillet test is the most commonly done motion palpation test. The intra-examiner reliability data suggests that the Gillet test is clinically useful for a single examiner in assessing the sacroiliac joint for mobility dysfunction especially at upper sacroiliac contact points. Linear regression analyses suggest that the test is sensitive in that reliability improves with increasing perceived abnormality.
Tion that the Gillet test assesses sacroiliac joint hypomo-bility and that it is the hypomobility rather than. Innominate torsion that leads to LBP. Special Tests Covered in this Lesson.
Sacral Thrust Test Compression Test Distraction Test Thigh Thrust Test Gaenslens Test StorkGillet Test Lasletts. Although mechanisms to assess sacroiliac joint motion do not currently exist investigators using these tests and those promoting test use in texts often suggest using one or more of what they call dynamic tests ie standing flexion test sitting flexion test Gillet test and supine-to-sit test to detect hypomobility or motion. Performing the TestThe examiner places hisher hands on each ASIS while maintaining hisher body over the hands.
Push inward at a 45 degree angle on both to engage the tissue. While maintaining the the position on one side on the opposite side continue to overpress in order to determine the mobility of the joint. Repeat on the opposite side.
Although sacroiliac joint dysfunction SIJD is generally regarded as a source of lumbar pain its anatomical position and the absence of a diagnostic gold standard lead to difficulties at examination and differential diagnosis. However since sacroiliac SI joint blocks only provide information about pathologies of joint origin and since SIJD developing secondary to pathologies in. Sacroiliac joint dysfunction or sacroiliitis are common terms used to describe the pain of the sacroiliac joint.
It is usually caused by abnormal motion ie. Hyper- or hypo-mobile or malalignment of the sacroiliac joint. Sacroiliac joint syndrome is a significant source of pain in 15 to 30 of people with mechanical low back pain.