B 5- U AC U U AC 3. By Biology experts to help you in doubts scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.

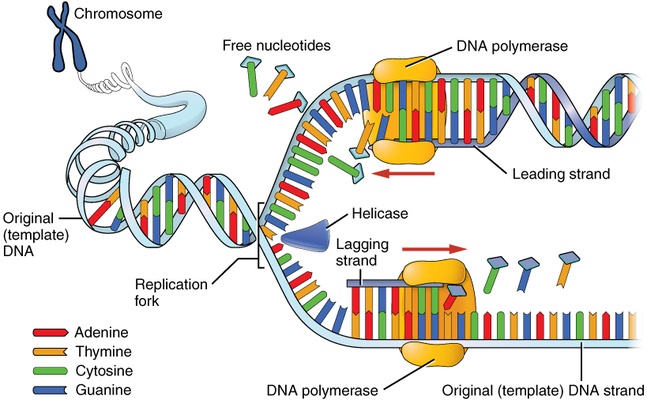
The diagram shows the base sequence of a strand of DNA.
If a strand of dna has the nitrogen base sequence. If a strand of dna has the nitrogen base sequence 5-atttgc-3 what will be the sequence of the matching strand. If a strand of dna has the nitrogen base sequence 5-atttgc-3 what will be the sequence of the matching strand. 3-atttgc-5 3-taaacg-5 3-uaaacg-5 3-tuuucg-5 3-gcaaat-5 submitrequest answer part b if a dna double helix is 100 nucleotide pairs long and contains 25 adenine.
If the sequence of nitrogen bases of the coding strand of DNA in a transcription unit is 5- ATGAATG-3 The sequence of bases in its RNA transcript would be. A 5 AU G AAU G 3. B 5- U AC U U AC 3.
If a strand of DNA has the nitrogen base sequence 5-ATTTGC-3 what will be the sequence of the matching strand. Step by step video text image solution for A DNA strand with nitrogenous base sequence ATTGCC will have. By Biology experts to help you in doubts scoring excellent marks in Class 12 exams.
Open Answer in App. First think about which base pairs arise in complementary strands of DNA. Adenine thymine A T thymine adenine T A cytosine guanine C G guanine cytosine G C However mRNA does not consist of the same four bases as DNA.
While DNA has the ATCG nitrogenous bases RNA replaces thymine with uracil making its bases AUCG. A portion of a gene on one strand of DNA has the following nitrogen base sequence. GCT-ACC-GAA-TAC Which nitrogen base sequence will most likely be transcribed on the messenger RNA molecule.
DNA has 4 nitrogen bases which are AdenineA GuanineG ThymineT CytosineC. RNA also has 4 bases but in RNA Uracil U is present instead thymine. Adenine always pair with thymine by twi hydrogen bonds in DNA and to Uracil in RNA.
The nitrogen bases can only pair in a certain way. A pairing with T and C pairing with G. Due to the base pairing the DNA strands are complementary to each other run in opposite directions and are called antiparallel strands.
Answer If a strand of DNA has the nitrogen base sequence 5-ATTTGC-3 what will be the sequence of the matching strand. 3-TAAACG-5 Most relevant text from all around the web. If a strand of DNA has the nitrogen base sequence 5-ATTTGC-3 what will be the sequence of the matching strand.
The sequence of nitrogen bases in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein. The sequence of amino acids determines the structure and function of a protein. In biology specifically in terms of genetics and DNA complementary means that the polynucleotide strand paired with the second polynucleotide strand has a nitrogenous base sequence that is the reverse complement or the pair of the other strand.
The coding or non-template strand is the DNA strand complementary to the template strand. It has the same sequence except for T for U substitutions as the mRNA. The Pr ibnow box is a sequence of six nucleotides TATAAT positioned at -10 that signals where transcription initiation should begin in prokaryotic DNA.
Usually DNA exists as double-strand. Two DNA strands are bound together by various interactions one major interaction being base pairing between the nitrogenous bases of the opposite strands. The sequence of nitrogenous bases on one strand of a DNA molecules double helix matches up in a particular way with the sequence on the other strand.
Adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine. Why do the nitrogenous bases pair in this specific way. The bases on each strand are joined to the bases on the other strand with hydrogen bonds but different bases have different chemical.
If one strand of DNA has the following nitrogen base sequence what is the nitrogen base sequence of its complimentary mRNA strand. DNA Strand I T - A - C - G - C - A - A - T - A - C - G - G - A - C -. What is a complementary DNA sequence.
Complementary Definition Biology In biology specifically in terms of genetics and DNA complementary means that the polynucleotide strand paired with the second polynucleotide strand has a nitrogenous base sequence that is the reverse complement or the pair of the other strand. Mutation any change in the sequence of DNA Mutagen any agent causing a mutation to occur Example Radiation Three types of mutations 1. The new DNA strand formed after DNA replication is an exact copy of its parent strand.
The diagram shows the base sequence of a strand of DNA. From left to right what is the sequence of the complementary strand of DNA in this molecule. T G A A C.
A C T T G. Sugar phosphate nitrogen base. Sugar phosphate protein.